An overview of the key parameters, including sensitivity and the impact of resistance.
Microphone Sensitivity
Definition: Sensitivity refers to the efficiency of a microphone's sound-to-electricity conversion, measured in decibels (dB). Based on standard microphone testing, 0 dB is equivalent to 1V. Therefore, all microphone sensitivity values are negative (e.g., -58 dB).
Sensitivity Range:
The typical sensitivity range for microphones is between
-28 dB and -66 dB, depending
on the application:
- Laptops: Require higher sensitivity, around -27 dB.
- Bluetooth Headsets: Lower sensitivity, approximately -62 dB.
Impact of Resistance (R) on Sensitivity
It's important to note that microphone sensitivity is not solely determined by the capsule itself but is also influenced by the resistance (R) in the circuit. The value of this resistance has a direct impact on sensitivity:
- A higher resistance value increases sensitivity.
- Using the same microphone with R values of 1kΩ and 2kΩ can result in a sensitivity difference of nearly 7 dB!
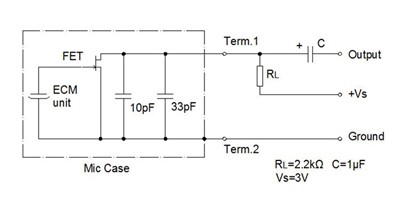
Test Conditions for Sensitivity
Since sensitivity is conditional, microphone manufacturers typically specify testing parameters. Common testing conditions include:
- Resistance (R): 2.2 kΩ
- Voltage: 3V
Electret microphones offer versatile performance, but their sensitivity depends not only on the capsule design but also on external factors like resistance and testing parameters. Properly aligning these variables ensures optimal functionality for diverse use cases.



