Definition: Frequency response refers to the consistency of a microphone's sensitivity across various points in the audio spectrum. The standard frequency response range for microphones is typically 20 Hz to 20 kHz. In general, the more consistent the sensitivity across this range, the flatter and better the frequency response curve is considered.
However, in practical applications, a flat frequency response curve is not always ideal. For example:
- Telephones: A microphone used in telephony often benefits from a "haystack-shaped" frequency response curve, which trims both the low and high ends. This design helps minimize low-frequency noise and high-end feedback.
- Aviation Headsets: The microphone in aviation headsets typically removes components below 700 Hz to avoid interference from the low-frequency noise of airplane engines.
- Conference Systems: For conference microphones, frequencies above 4 kHz are often reduced to mitigate feedback issues.
- Ultrasonic Transmission: In applications like ultrasound, the microphone's frequency response must be tailored to meet the requirements of specific high-frequency ranges.
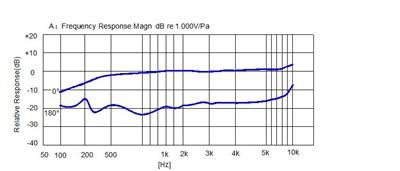
Optimizing Frequency Response for Applications
By customizing the frequency response to suit the intended application, microphones can achieve optimal performance in diverse environments. Whether it's enhancing speech clarity, reducing noise, or transmitting ultrasonic signals, selecting the right frequency response curve is essential for achieving desired outcomes.



