A microphone capsule (transducer) is a device that converts sound into an electrical signal. It is one of the most critical components in audio equipment, responsible for capturing sound and enabling further audio processing, such as amplification or recording.
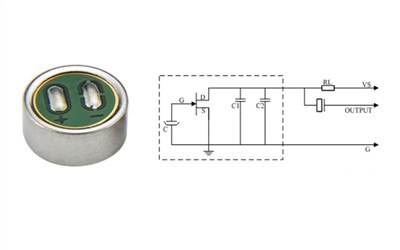
The microphone capsule consists of a small diaphragm and a capacitor inside. The diaphragm is typically made from a lightweight, flexible material that is sensitive to sound waves. When sound waves hit the diaphragm, they cause it to vibrate. This vibration results in a change in the distance between the diaphragm and a fixed capacitor plate, altering the capacitance between them.
As the capacitance changes, an electrical signal is generated. This is the fundamental principle behind how a microphone capsule converts sound into an electrical signal. The electrical signal produced is a representation of the sound wave that was captured by the diaphragm.
Once the sound is converted into an electrical signal, it can be transmitted via cables to audio equipment such as amplifiers, mixers, or recording devices. This allows the sound to be either amplified for playback or stored for later use, such as in music production, broadcasting, or sound recording.
How the Microphone Capsule Works:
- Sound Wave Detection: The microphone capsule detects sound waves through its diaphragm.
- Diaphragm Vibration: The diaphragm vibrates in response to sound waves, causing a change in the capacitance.
- Capacitance Change: The change in capacitance creates an electrical signal that mirrors the original sound wave.
- Signal Transmission: The electrical signal is transmitted to other audio equipment for amplification or recording.
In conclusion, the microphone capsule plays a crucial role in transforming sound into a usable electrical signal, which is essential for any audio application, from public address systems to high-fidelity sound recording.



