Ever wondered how a microphone (mic head) turns sound into something your devices can use? Let's break down a typical microphone circuit and see how it senses, amplifies, and processes sound signals.
Different types of microphones, like dynamic, condenser, and electret, have slightly different setups. But here's a look at what most microphone circuits have in common:
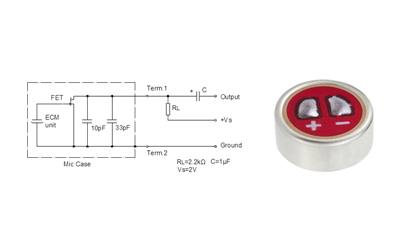
The Key Parts of a Microphone Circuit
A typical microphone circuit includes the following key components:
1. Microphone Element (Mic Head)
This is where the magic starts! The mic head picks up sound waves and converts them into an electrical signal. Different microphones do this in different ways:
- Dynamic Microphones: They work like little generators. Sound waves move a coil inside a magnetic field, creating an electric current.
- Condenser (Electret) Microphones: These use changes in capacitance caused by sound waves to generate a signal. Think of it like a tiny capacitor that reacts to sound.
2. Preamplifier (Preamp)
The signal coming from the mic head is usually pretty weak. That's where the preamp comes in. It boosts the signal so that it's strong enough for further processing. A good preamp is key to getting clear, noise-free audio.
3. Biasing Circuit
Some microphones, like electret condensers, need a small amount of DC voltage to work. The biasing circuit supplies this power to keep everything running smoothly.
4. Filter Circuit
No one likes noisy audio! The filter circuit helps clean up the signal by removing unwanted noise and interference, making sure you get a clear sound.
5. Output Circuit
Finally, the output circuit takes the processed signal and sends it to whatever device is next in line-be it an audio amplifier, recording gear, or digital converter.
Putting It All Together: How an Electret Microphone Circuit Works
- Catching the Sound: The microphone element senses the sound waves around it and turns them into an electrical signal.
- Amplifying the Signal: This weak signal is then boosted by the preamp, making it stronger and clearer.
- Cleaning Up the Audio: The amplified signal might pass through a filter circuit to cut out any noise or interference.
- Sending It Out: After all this processing, the clean signal is sent out through the output circuit to your next device.
Keep in Mind: The exact design of a microphone circuit can vary based on the type of mic, what it's being used for, and other factors like cost. So, if you're designing one yourself, be sure to customize and optimize it for your specific needs!



